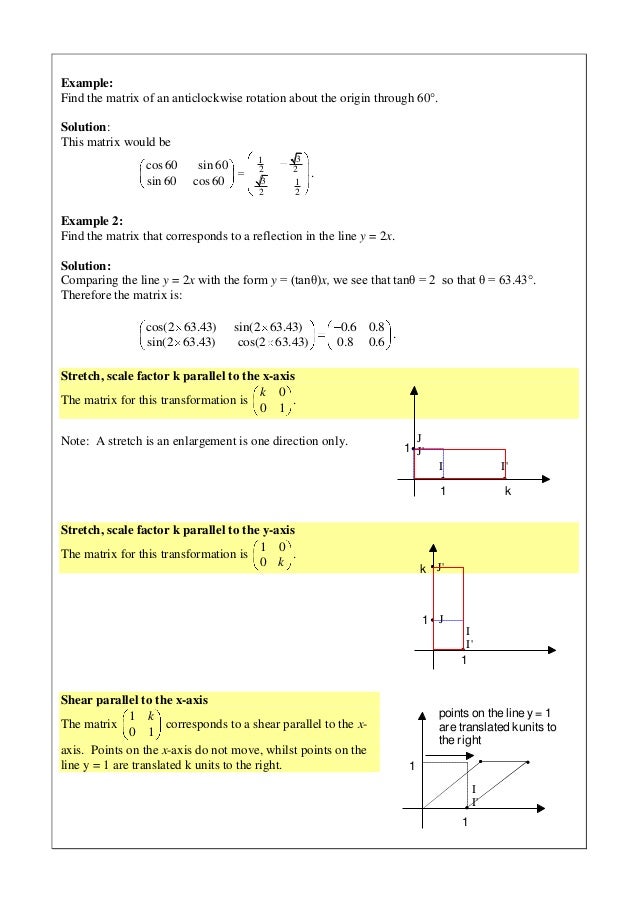
Usually you should just use these two rules T (x)T (y) = T (xy) cT (x) = T (cx) Where T is your transformation (in this case, the scaling matrix), x and y are two abstract column vectors, and cQuestion Question 4 10 Points Suppose T Is A Transformation From R2 To R2 Find The Matrix A That Induces T If I Is A) Reflection Over The Line Y=5x B) Rotation By 1/41 0 0 A) A = 0 0 0 0 B) A = 0 0 This problem has been solved!In this lesson we talked about how to reflect a point in the line y=x In this lesson we talked about how to reflect a point in the line y=x
Transformation Of Graphs Using Matrices Reflection
How to find transformation matrix for reflection
How to find transformation matrix for reflection-Reflection It is a transformation which produces a mirror image of an object The mirror image can be either about xaxis or yaxis The object is rotated by180° Types of Reflection Reflection about the xaxis;Tutorial on transformation matrices and reflections on the line y=xYOUTUBE CHANNEL at https//wwwyoutubecom/ExamSolutionsEXAMSOLUTIONS WEBSITE at https//w



2d Shearing In Computer Graphics Definition Examples Gate Vidyalay
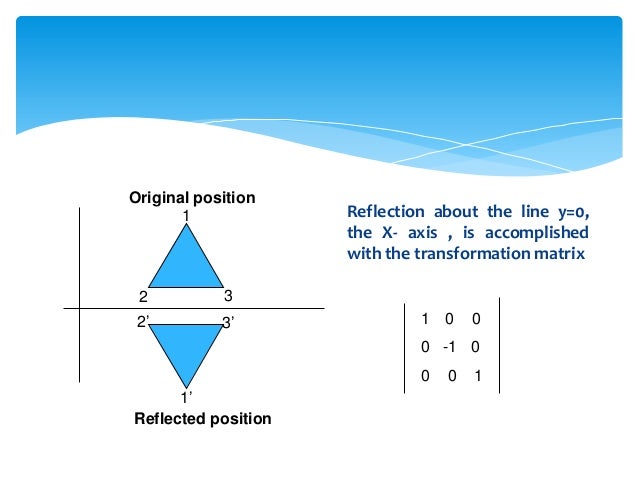
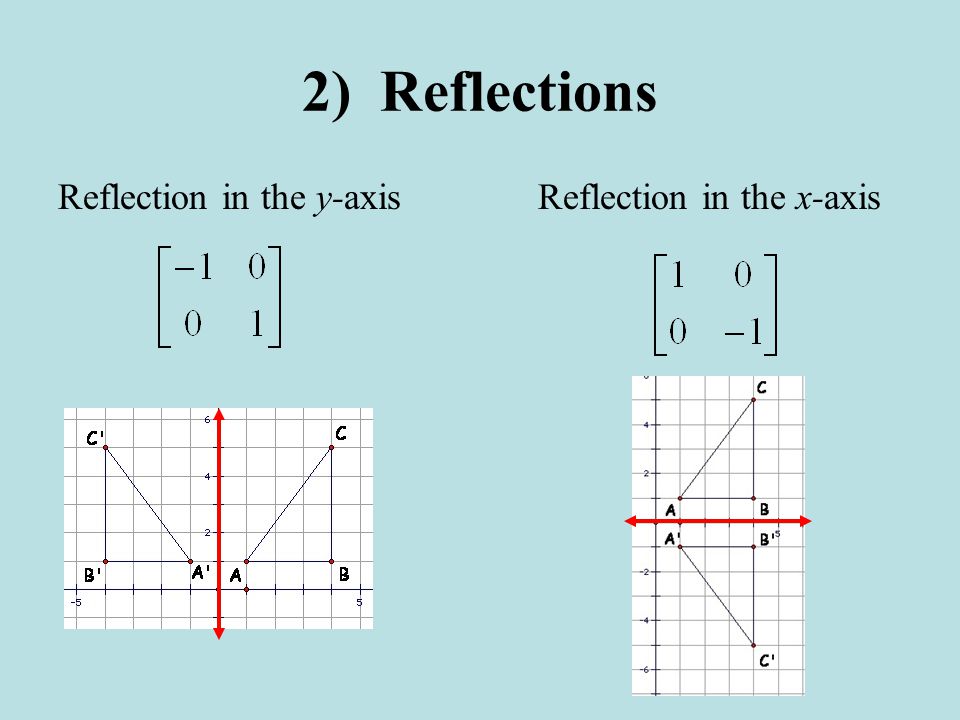
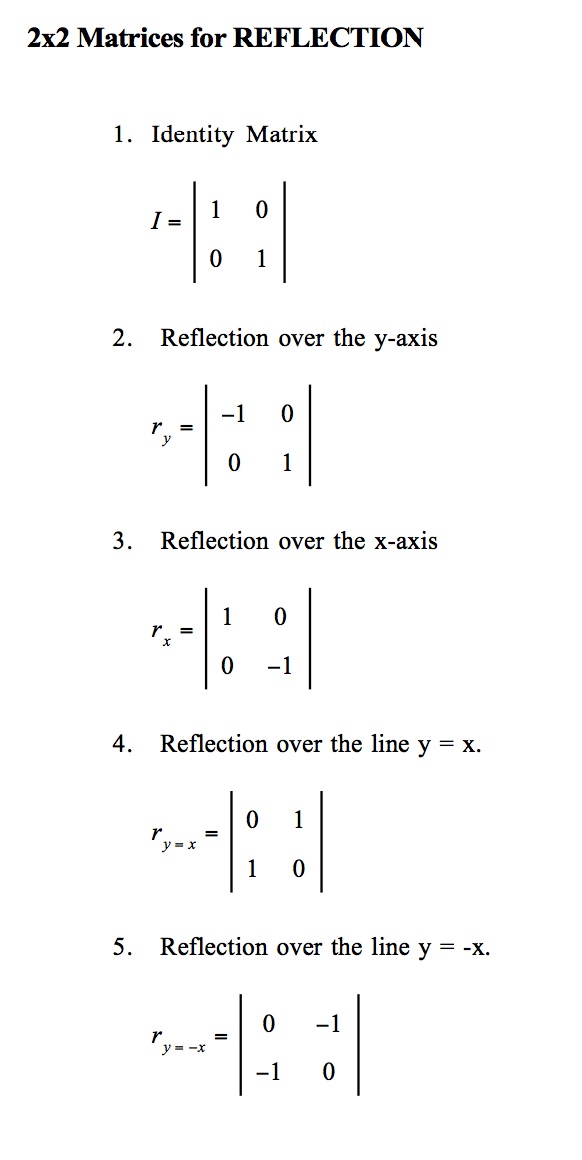
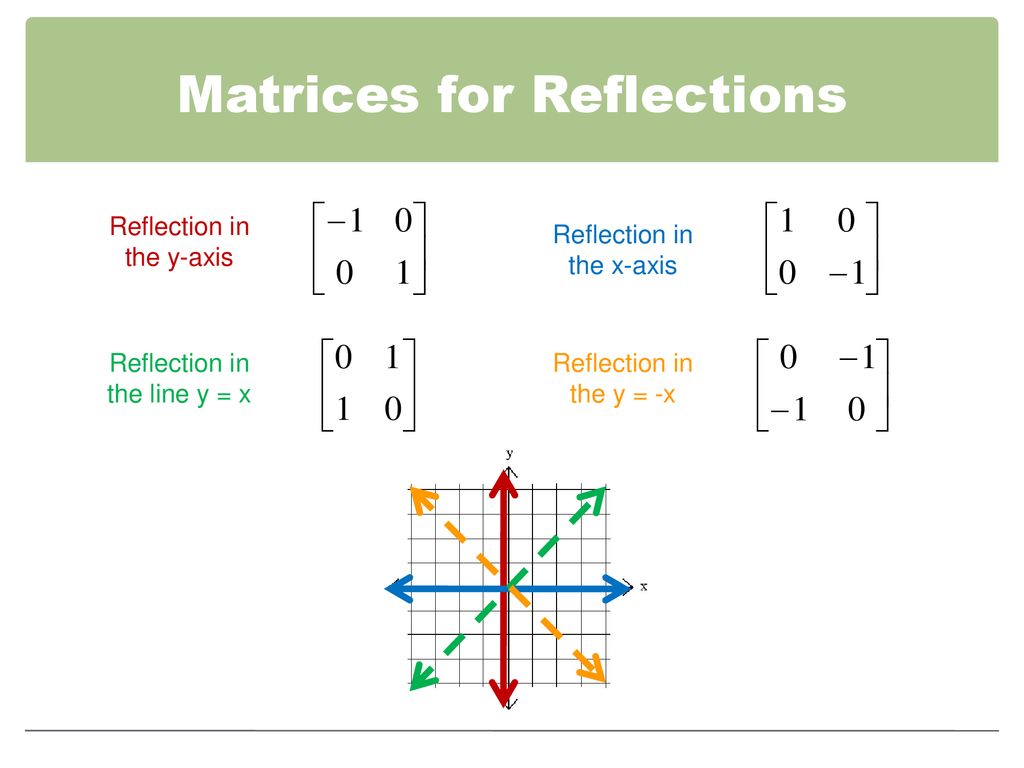
Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question Which of the following is a single transformation matrix of the composition of transformations, reflection over the line y = x followed by rotation of 90° about the origin?For the of the reader, we note that there are other ways of "deriving" this result One is by the use of a diagram, which would show that (1, 0) gets reflected to (cos 2 θ, sin 2 θ) and (0, 1) gets reflected to (sin 2 θ,cos 2 θ)Another way is to observe that we can rotate an arbitrary mirror line onto the xaxis, then reflect across the xaxis, andY –x (x, y) → (–y, –x) It is easy to prove that the matrices for r x, r y = x, and r y = – x are as stated in the next theorem Matrices for r x, r y=x, and r y=–x Theorem 1 10 0 –1 is the matrix for r x 2 01 10 is the matrix for r y = x 3 0 –1 –1 0 is the matrix for r y = –x Proof of 1 10 0 –1 x y = 1 x 0 y 0 x –1 y = x –y
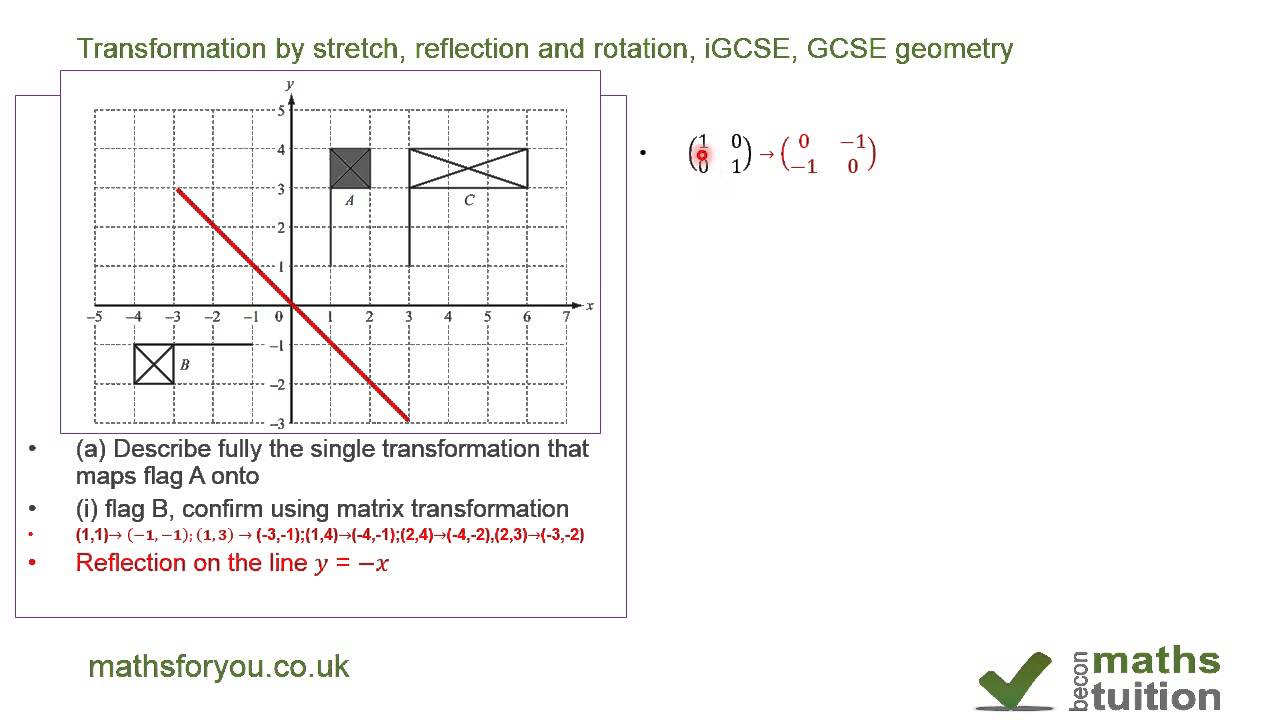
(A) (B) b 1910 ) d ОА B С D Which of the following matrices can be used for a single transformation of translation of aBrowse 165 sets of matrices transformations flashcards Study sets Diagrams Classes Users 10 Terms melanie_james5 Matrices for transformations Change the sign of the yvalue Change the sign of the xvalue Flip x and y values ( just flip them ) Flip x and y values and change the signs A series of reflections is modeled by successive mirror matrix multiplications If light bounces off mirror 1, then 2 then 3, the net effect of these three reflections is k 4 M 3 M 2 M 1 k 1 which reduces to a single effective mirror matrix M eff M 3 M 2 M 1 2 So the effect of any set of mirrors can be reduced to a single 3x3
Tutorial on transformation matrices in the case of a reflection on the line y=xYOUTUBE CHANNEL at https//wwwyoutubecom/ExamSolutionsEXAMSOLUTIONS WEBSITThe transformation matrix is used for_____ A Reflection at X axis B Reflection at Y axis C Reflection at origin D None of these ANSWER B The transformation matrix is used for_____ A Reflection at X axis B Reflection at Y axis C Reflection at origin D Reflection at line Y=X ANSWER C The transformation matrix is used for_____So rotation definitely is a linear transformation, at least the way I've shown you Now let's actually construct a mathematical definition for it Let's actually construct a matrix that will perform the transformation So I'm saying that my rotation transformation from R2 to R2 of some vector x can be defined as some 2 by 2 matrix




Transformations With Matrices Easing The Hurry Syndrome



Schoolwires Henry K12 Ga Us Cms Lib08 Ga Centricity Domain 26 7th and 8th grade math 8th grade flexbook Unit 1 sections 1 23 1 4 rules for reflections Pdf
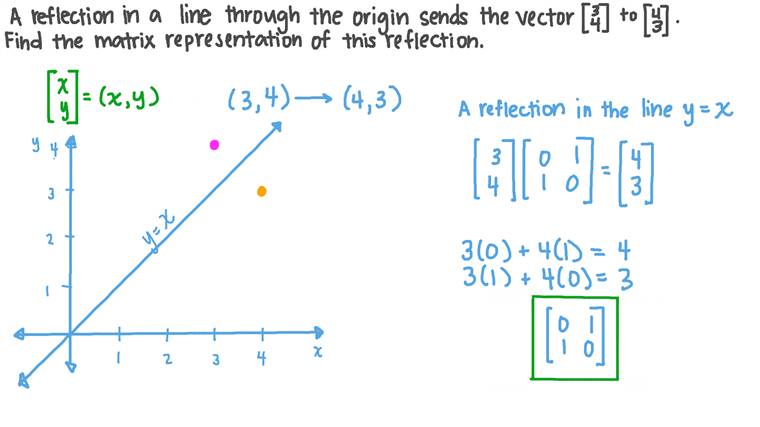
Let T R 2 → R 2 be a linear transformation of the 2 dimensional vector space R 2 (the x y plane) to itself which is the reflection across a line y = m x for some m ∈ R Then find the matrix representation of the linear transformation T with respect to the standard basis B = { e 1, e 2 } of R 2, where e 1 = 1 0, e 2 = 0 1Y x It determines the linear operator T(x;y) = ( y;x) In particular, the two basis vectors e 1 = 1 0 and e 2 = 0 1 are sent to the vectors e 2 = 0 1 and e 2 = 1 0 respectively Note that these are the rst and second columns of A You'll recognize this transformation as a rotation around the origin by 90Step 1 First we have to write the vertices of the given triangle ABC in matrix form as given below Step 2 Since the triangle ABC is reflected about xaxis, to get the reflected image, we have to multiply the above matrix by the matrix given below Step 3 Now, let us multiply the two matrices Step 4



Transformation Matrices Reflection The Line Y X Examsolutions Maths Tutorials Youtube



Find The Matrix For The Linear Transformation Which Chegg Com
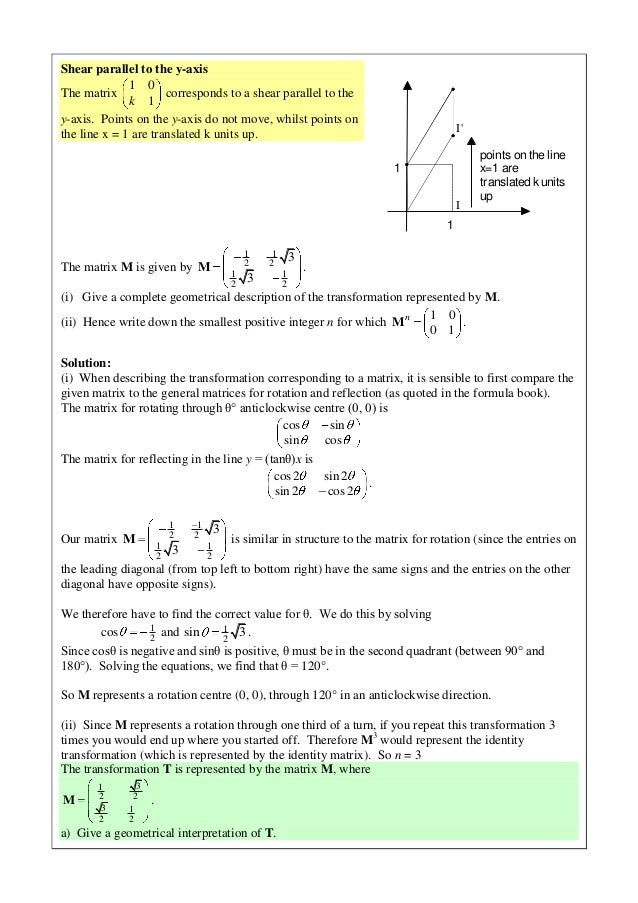
1 Let Υ R 3 → R 3 be a reflection across the plane π − x y 2 z = 0 Find the matrix of this linear transformation using the standard basis vectors and the matrix which is diagonal Now first of, If I have this plane then for Υ ( x, y, z) = ( − x, y, 2 z) I get this when passing any vector, so the matrix using standard basis vectors is Y = ( − 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 − 2)Visualize what the particular transformation is doing Example 6 Describe in geometrical terms the linear transformation defined by the following matrices a A= 0 1 −1 0 This is a clockwise rotation of the plane about the origin through 90 degrees b A= 2 0 0 1 3 Ax 1,x 2T = 2x 1, 1 3 x 2 T This linear transformation stretches theDerive the matrix in 2D for Reflection of an object about a line y=mxc written 25 years ago by profvaibhavbadbe ♦ 780 modified 14 months ago by sanketshingote ♦ 570 2d transformation matrix




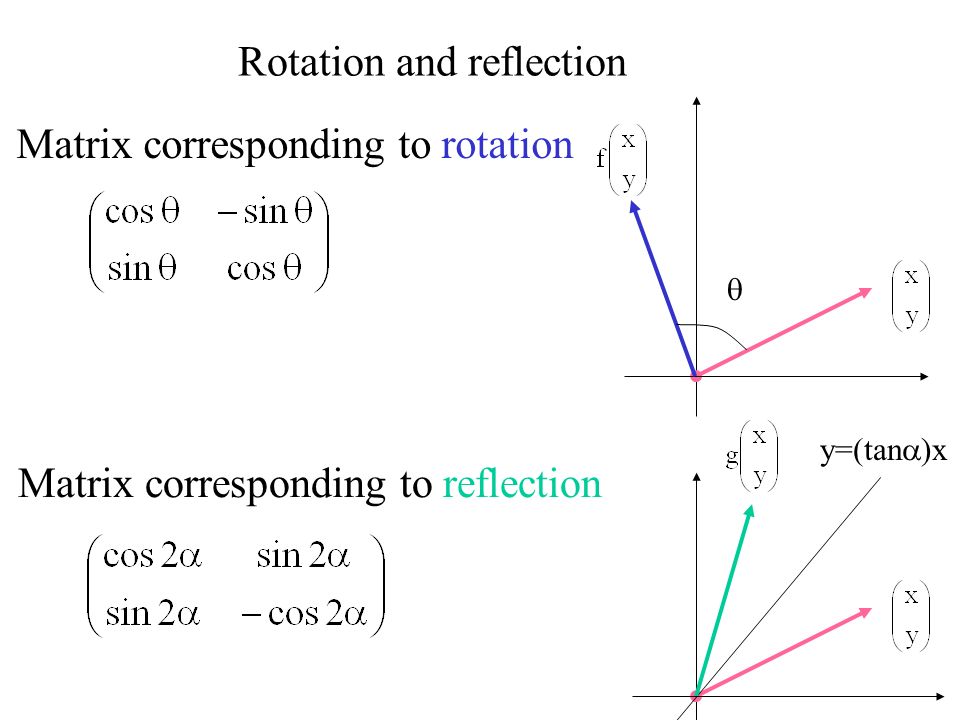
Matrix Corresponding To Rotation Matrix Corresponding To Reflection Rotation And Reflection Y Tan X Ppt Download



Matrices In Computer Graphics Dalao S World
M ×n matrix A to define a transformation TARn → Rm in this manner In the next section we will see that such transformations have a desirable characteristic, and that every transformation with that characteristic can be represented by multiplication by a matrix 901 Linear Transformations A function is a rule that assigns a value from a set B for each element in a set A Notation f A 7!B If the value b 2 B is assigned to value a 2 A, then write f(a) = b, b is called the image of a under f A is called the domain of f and B is called the codomain The subset of B consisting of all possible values of f as a varies in the domain is called the range ofReflection about line y=x;



Reflection Rules How To W 25 Step By Step Examples



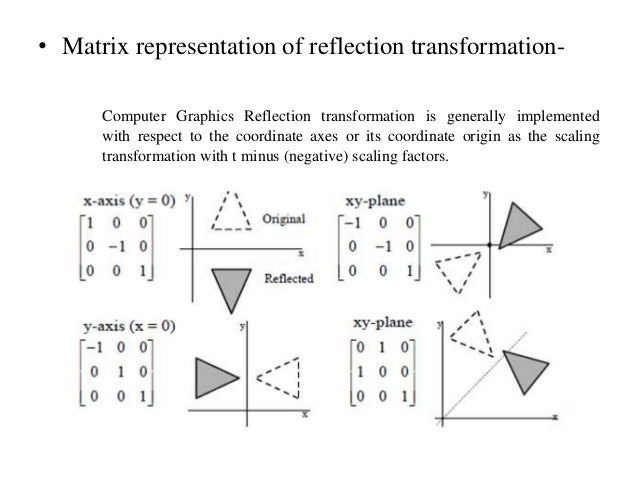
Determine The Transformation Matrix For The Reflection Computer Graphics
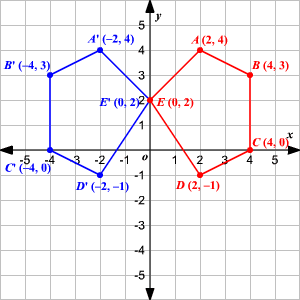
Composition of Transformations The symbol for a composition of transformations (or functions) is an open circle A notation such as is read as "a translation of (x, y) → (x 1, y 5) after a reflection in the line y = x" You may also see the notation written as This process must be done from right to leftReflectionMatrixv gives the matrix that represents reflection of points in a mirror normal to the vector vTransformations and Matrices A matrix can do geometric transformations!




What Is A Linear Transformation Quora



Do You Know Matrix Transformations
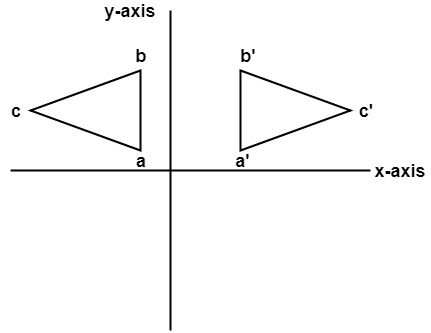
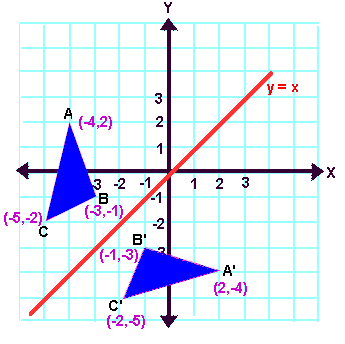
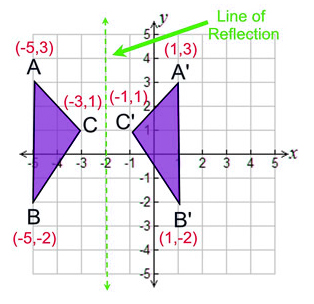
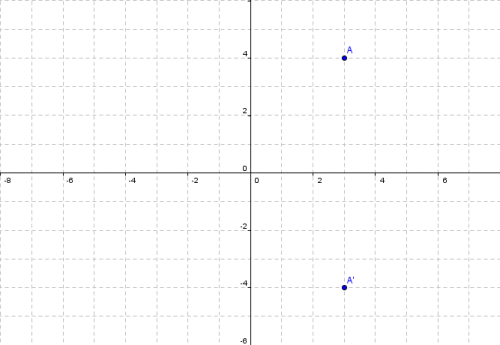
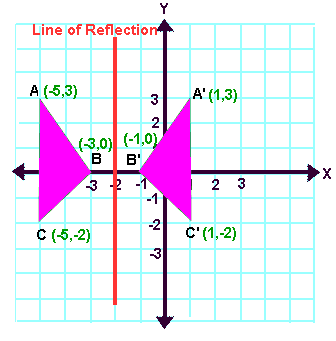
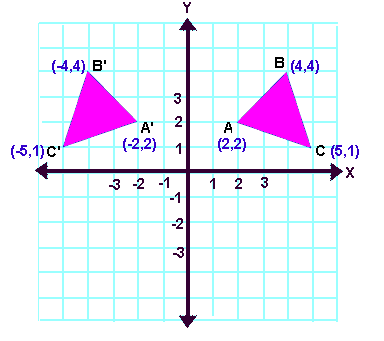
The handout, Reflection over Any Oblique Line, shows the derivations of the linear transformation rules for lines of reflection y = √ (3)x – 4 and y = 4/5x 4 Line y = √ (3)x – 4 θ = Tan 1 (√ (3)) = 60° and b = 4 The corresponding linear transformation rule is (p, q) → (r, s) = (05p 0866q 3464, 0866p 05q – 2) Let T R 2 →R 2, be the matrix operator for reflection across the line L y = x a Find the standard matrix T by finding T(e1) and T(e2) b Find a nonzero vector x such that T(x) = x c Find a vector in the domain of T for which T(x,y) = (3,5) Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution a I found T = 0 11 0 bIf (a, b) is reflected on the line y = x, its image is the point (b, a) If (a, b) is reflected on the line y = x, its image is the point (b, a) Geometry Reflection A reflection is an isometry, which means the original and image are congruent, that can be described as a "flip"



Computer Graphics Reflection Javatpoint




Matrix Corresponding To Rotation Matrix Corresponding To Reflection Rotation And Reflection Y Tan X Ppt Download
Problem 1 Find a linear transformation rule of the form (p, q) → (r, s) such that the reflection image of the point (p, q) over the oblique line y = mx b is the point (r, s) In the general case, both r and s are functions of p, q, m and bFor a reflection over the x − axis y − axis line y = x Multiply the vertex on the left by 1 0 0 − 1 − 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0Get the free "Reflection Calculator MyALevelMathsTutor" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Education widgets in WolframAlpha



Computer Graphics Reflection Javatpoint



Reflection In 2 D
Have a play with this 2D transformation app Matrices can also transform from 3D to 2D (very useful for computer graphics), do 3D transformations and much much more The Mathematics For each x,y point that makes up the shape we do this matrix multiplicationReflection Transformations in 2Space Let such that and suppose that we want to reflect across the axis as illustrated Thus the coordinate of our vector will be the opposite to that of our image The following equations summarize our image Thus our standard matrix is , and in form we get that Of course there are other types of reflectionTo reflect a point through a plane = (which goes through the origin), one can use =, where is the 3x3 identity matrix and is the threedimensional unit vector for the vector normal of the plane If the L2 norm of ,, and is unity, the transformation matrix can be expressed as = Note that these are particular cases of a Householder reflection in two and three dimensions



Transformation Matrix For Stretch Reflection And Rotation Igcse Gcse High School Geomery Youtube



Reflection Transformation Matrix
Reflection about an axis perpendicular to xy plane and passing through the origin;3 ⋅ x 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 y 1 y 2 y 3 y 4 When we want to create a reflection image we multiply the vertex matrix of our figure with what is called a reflection matrix The most common reflection matrices are for a reflection in the xaxis 1 0 0 − 1 for a reflection in the yaxis − 1 0 0 1D (1) = 0 = 0*x^2 0*x 0*1 The matrix A of a transformation with respect to a basis has its column vectors as the coordinate vectors of such basis vectors Since B = {x^2, x, 1} is just the standard basis for P2, it is just the scalars that I have noted above A= 0 0 0



3d Transformation



Math Alive Geometry 1
12 Finding the matrix to represent a transformation To find the matrix that defines a transformation you find the images of the two points I(1, 0) and J(0, 1) The image of (1, 0) forms the first column of the matrix The image of (0, 1) forms the second column of the matrix Example Find the matrix that represents a reflection in the yaxisGraph functions using reflections about the xaxis and the yaxis Another transformation that can be applied to a function is a reflection over the x – or y axis A vertical reflection reflects a graph vertically across the x axis, while a horizontal reflection reflects a graph horizontally across the yMore Matrix Transformations Fill in the matrices for the following transformations Transformation Matrix Transformation Matrix A Reflection in the x axis ⎛⎞ ⎜⎟ ⎝⎠ N Rotation by 45°clockwise about the origin ⎛⎞ ⎜⎟ ⎝⎠ B Rotation by 30°clockwise about the origin ⎛⎞ ⎜⎟ ⎝⎠ O Reflection in the y axis



4 4 Transformations With Matrices Ppt Video Online Download




Chapter 4 Chapter Content 1 Real Vector Spaces
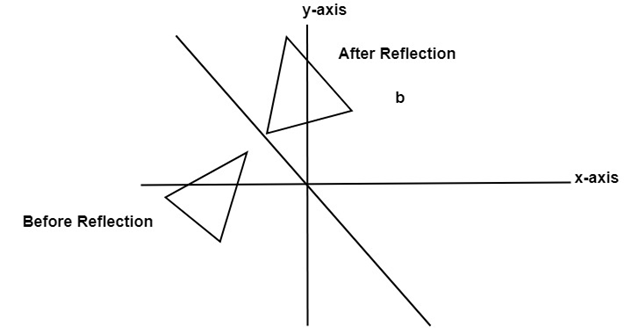
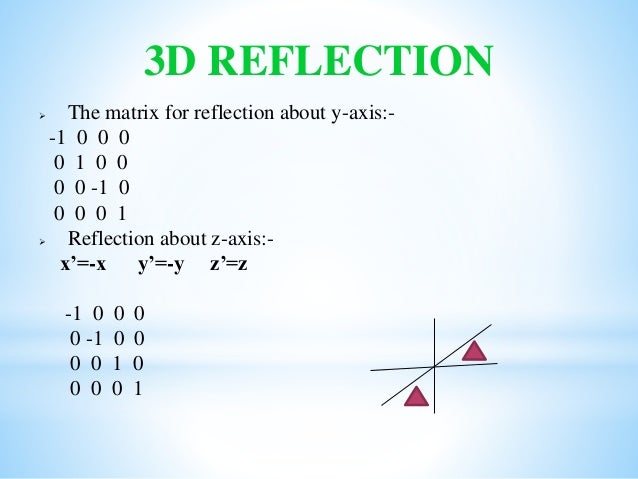
See the answer Show transcribed image text3D Reflection in Computer Graphics Reflection is a kind of rotation where the angle of rotation is 180 degree The reflected object is always formed on the other side of mirror The size of reflected object is same as the size of original object Consider a point object O has to be reflected in aReflection about the line y=x Once students understand the rules which they have to apply for reflection transformation, they can easily make reflection transformation of a figure For example, if we are going to make reflection transformation of the point (2,3) about xaxis, after transformation, the point would be (2,3)




March 18 Visicomp Codder




Graphics 2 D Geometric Transformations Cgvr Korea Ac
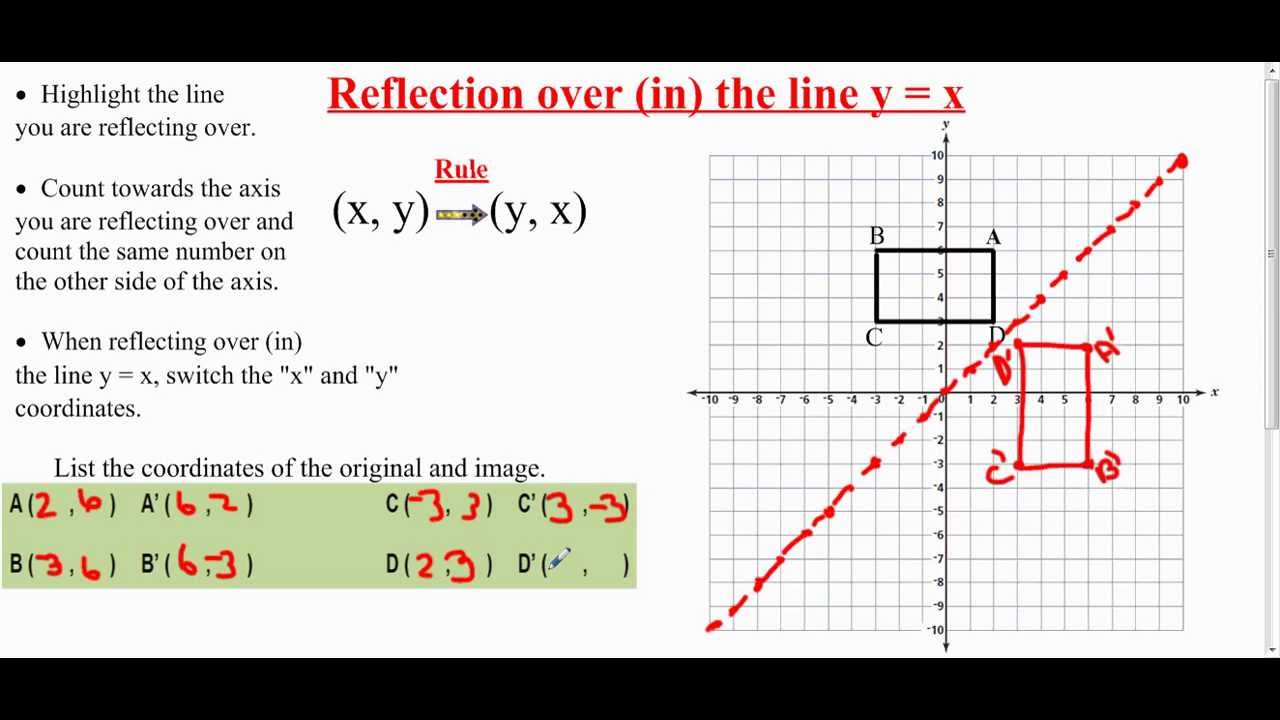
Geometry reflection A reflection is a "flip" of an object over a line Let's look at two very common reflections a horizontal reflection and a vertical reflectionThe Matrix of a Linear Transformation We have seen that any matrix transformation x Ax is a linear transformation The converse is also true Specifically, if T n m is a linear transformation, then there is a unique m n matrix, A, such that T x Ax for all x n The next example illustrates how to find this matrixThis video demonstrates how to reflect a figure over the line y=x It shows two methods of reflecting over y=x The video shows how to count towards the y=x
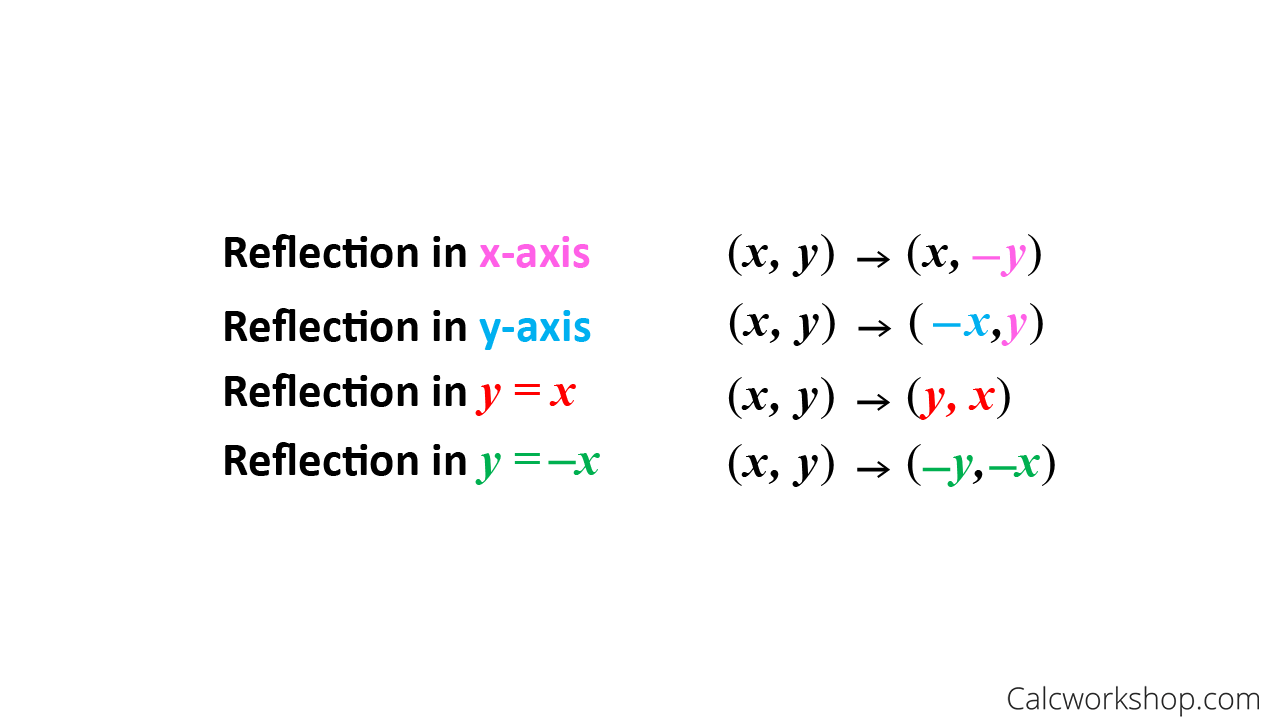



Reflection Rules How To W 25 Step By Step Examples



Do You Know Matrix Transformations
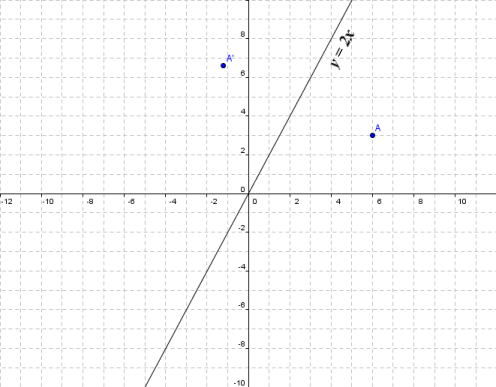
The linear transformation matrix for a reflection across the line $y = mx$ is $$\frac{1}{1 m^2}\begin{pmatrix}1m^2&2m\\2m&m^21\end{pmatrix} $$ My professor gave us the formula above with no explanation why it works I am completely new to linear algebra so I have absolutely no idea how to go about deriving the formulaReflection about the yaxis;



Www Math Utah Edu Bertram 5270 Emre



Bestmaths



Reflection Definition Reflection In The Coordinate Plane



Matrices As Transformations



Helps For Making A Computer Animated Video Reflection Matrices Here



Matrices As Transformations




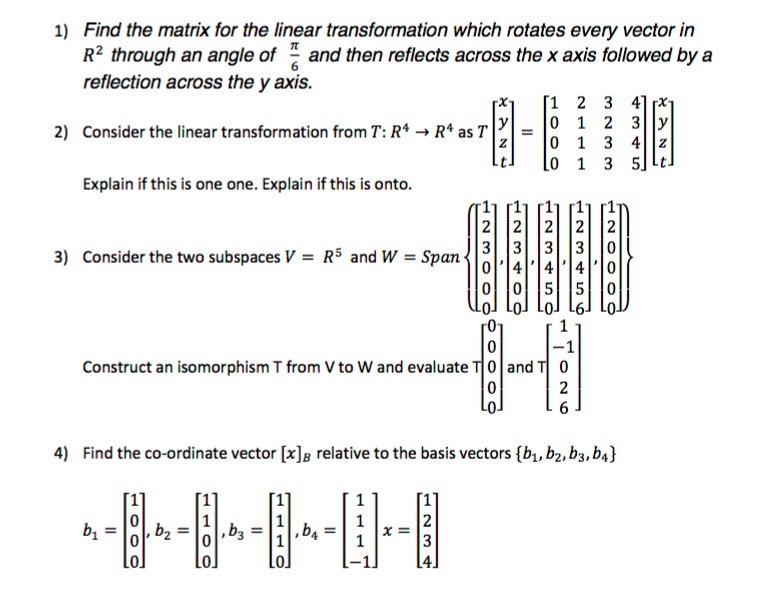
Match Each Linear Transformation With Its Matrix Chegg Com




Transformation Of Graphs Using Matrices Reflection
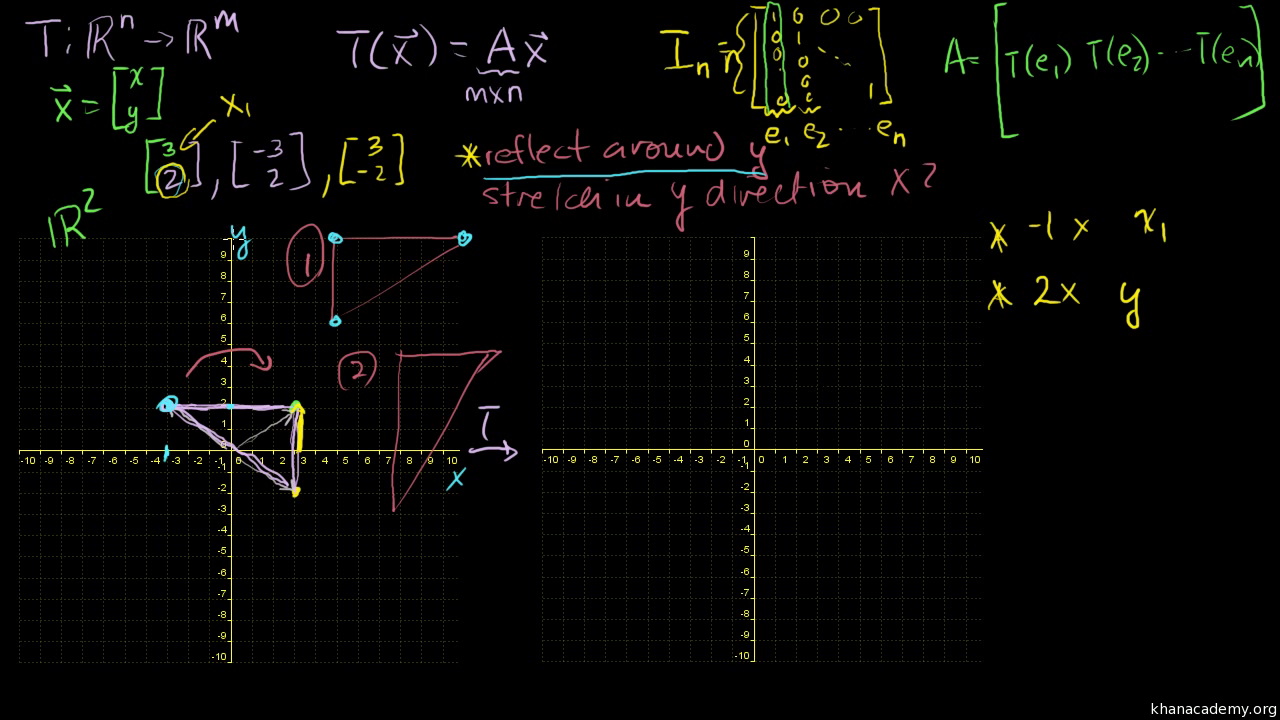



Linear Transformation Examples Scaling And Reflections Video Khan Academy
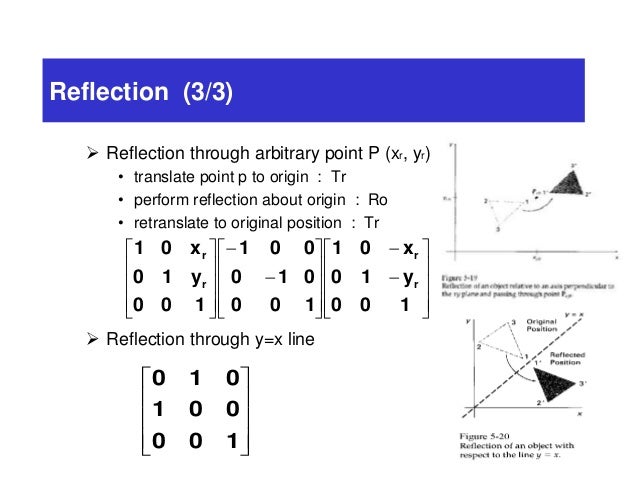



Two Dimensionaltransformations



Www Cgsd Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 215 Dataid 1165 Filename 255 Smp Seaa C04l06 Pdf
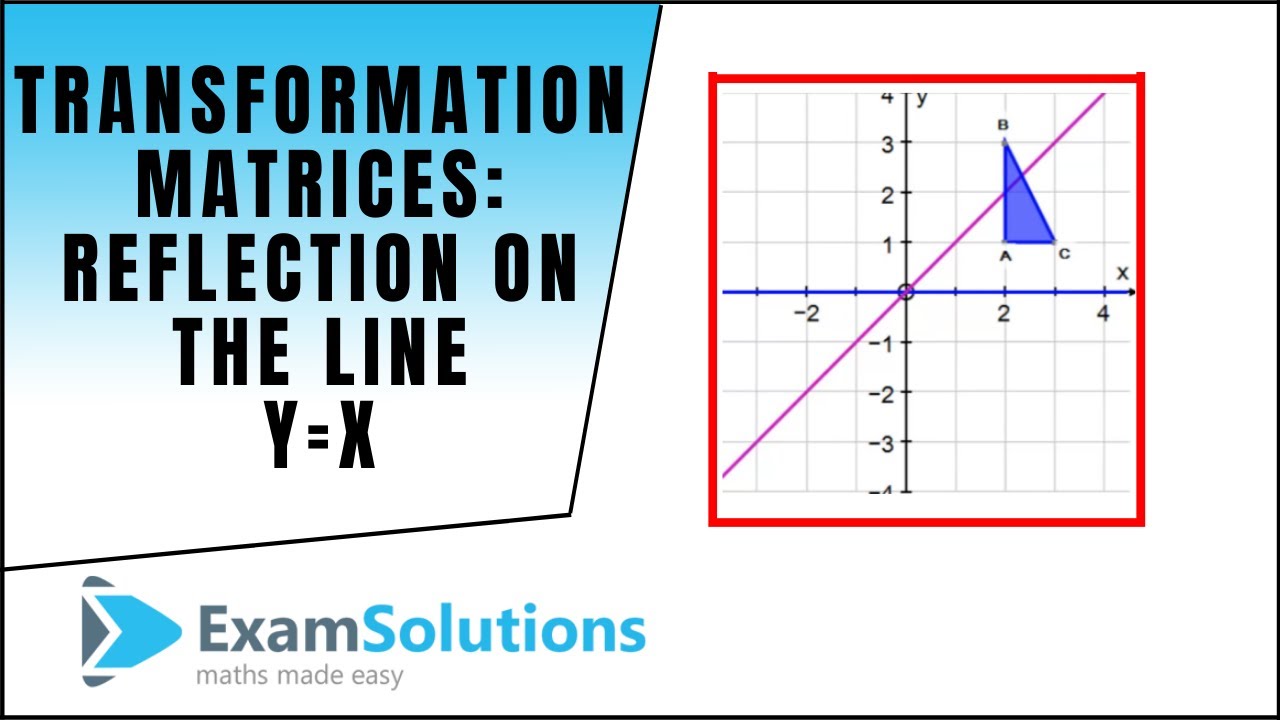



Transformation Matrices Reflection The Line Y X Examsolutions Maths Tutorials Youtube
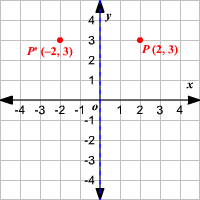



Reflections
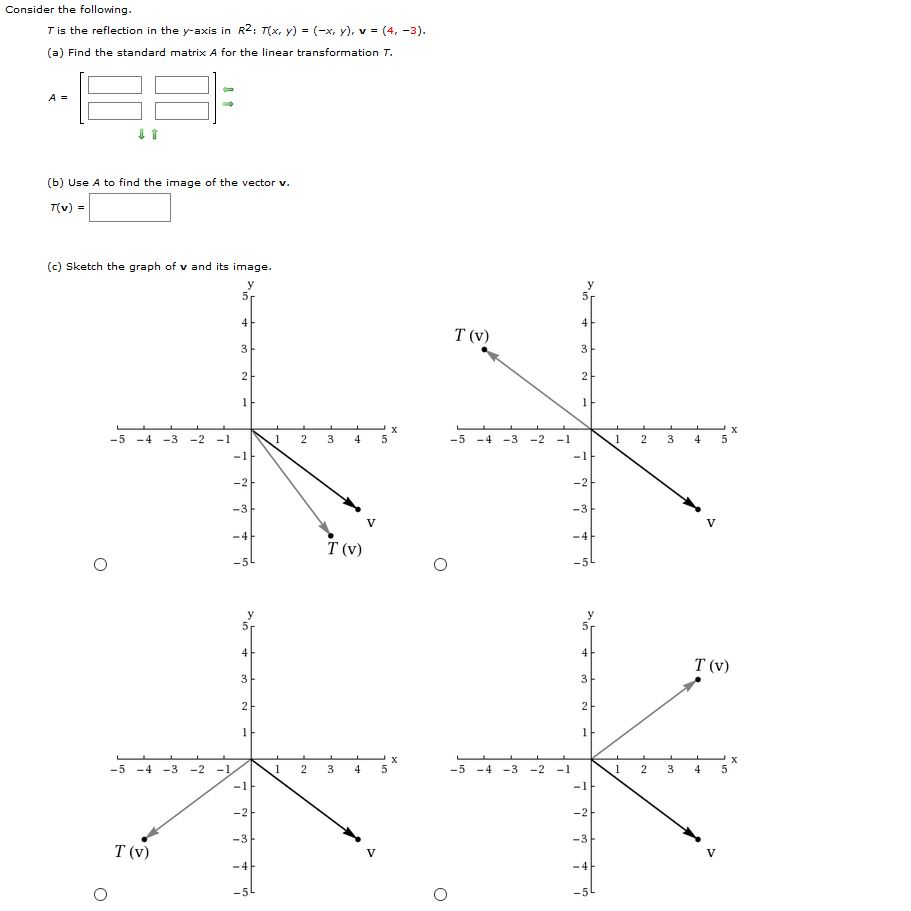



Consider The Following T Is The Reflection In The Chegg Com



Reflection Transformation



Spatial Transformation Matrices



Http Web Yonsei Ac Kr Hgjung Lectures Mat3 06 linear transformations Pdf



Reflection Transformation Matrix




Matrix Representation Of 2d Transformation Javatpoint



Lesson Linear Transformations In Planes Reflection Nagwa




Line Of Reflection Y 0 Novocom Top
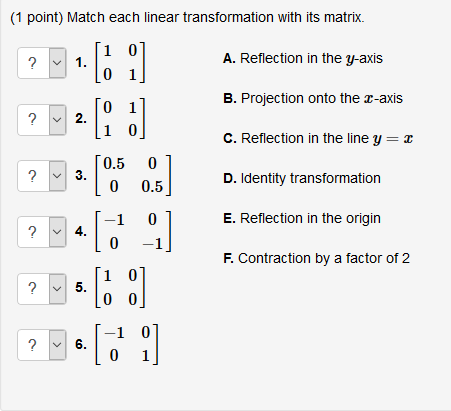



Match Each Linear Transformation With Its Matrix A Chegg Com




2 4 Modeling Motion With Matrices Pre Calc A Vocabulary Transformations Translation Reflection Rotations Dilations Ppt Download
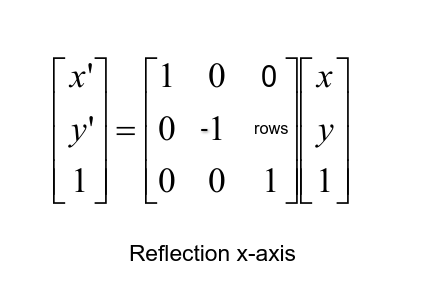



Image Transformations Using Opencv In Python Python Code
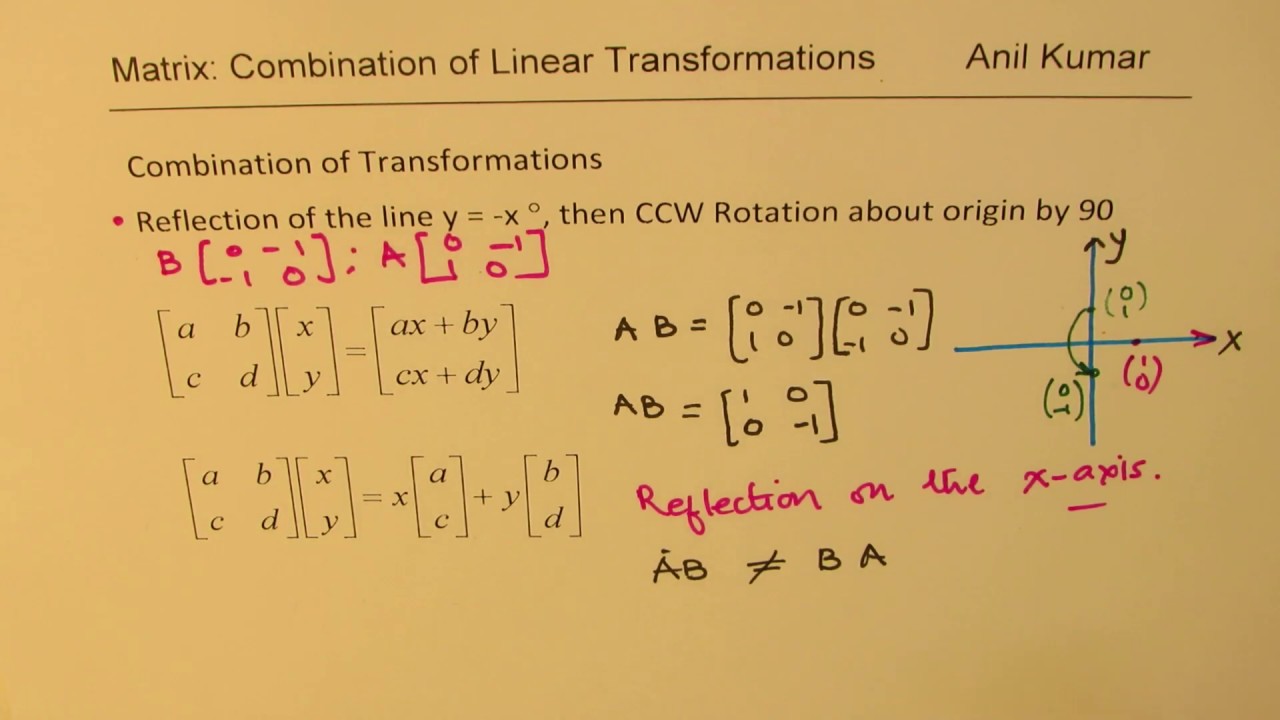



Linear Transformation Combination Of Ccw 90 Rotation And Reflection On Y X With Product Of Matrix Youtube




2d Transformation Tutorialspoint



Reflection Transformation Matrix




Rotation Matrix Wikipedia



Transformation Reflection Over The Line Y X Youtube



4 4 Geometric Transformations With Matrices Ppt Download



Matrix Corresponding To Rotation Matrix Corresponding To Reflection Rotation And Reflection Y Tan X Ppt Download
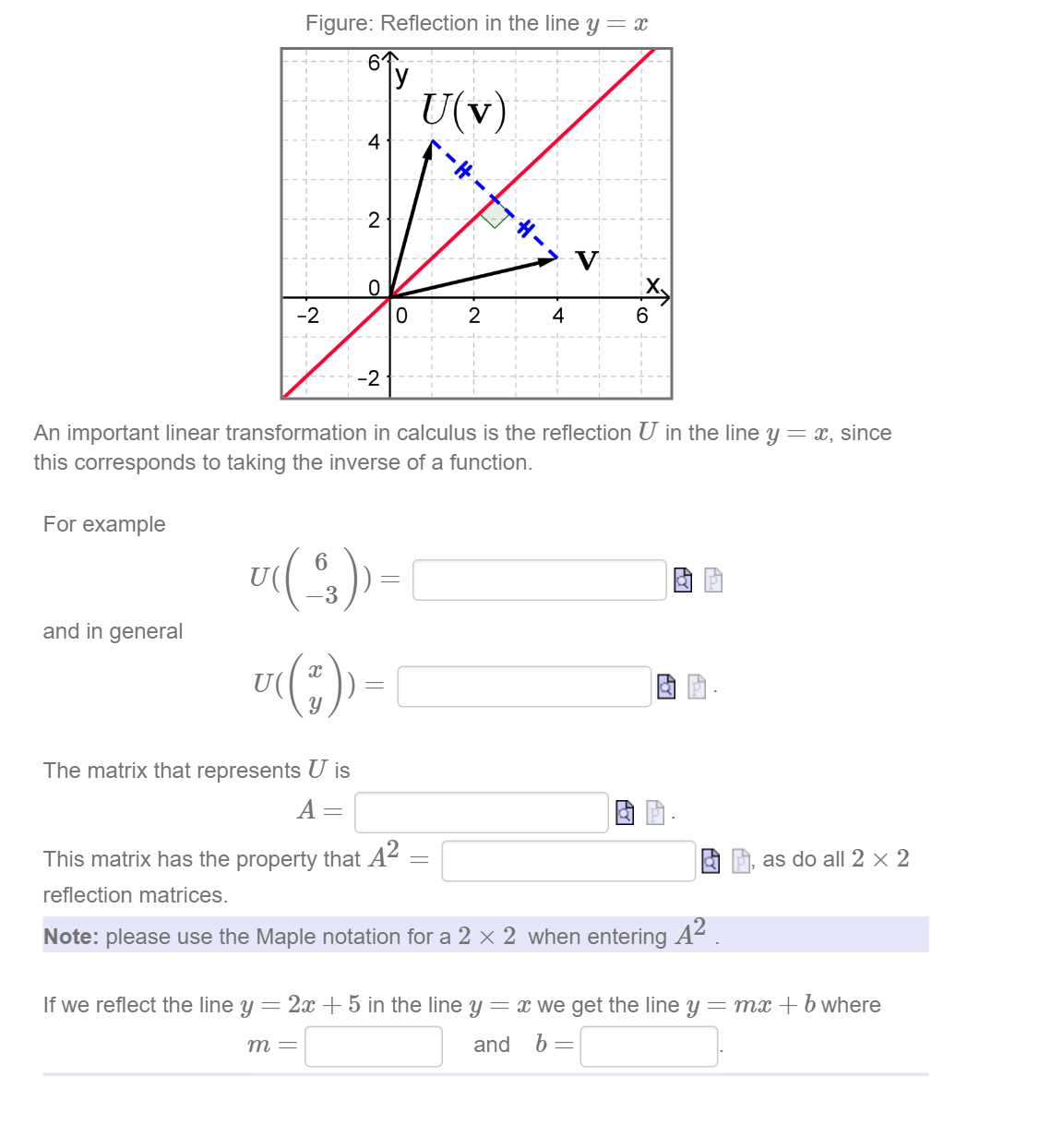



An Important Linear Transformation In Calculus Is The Chegg Com
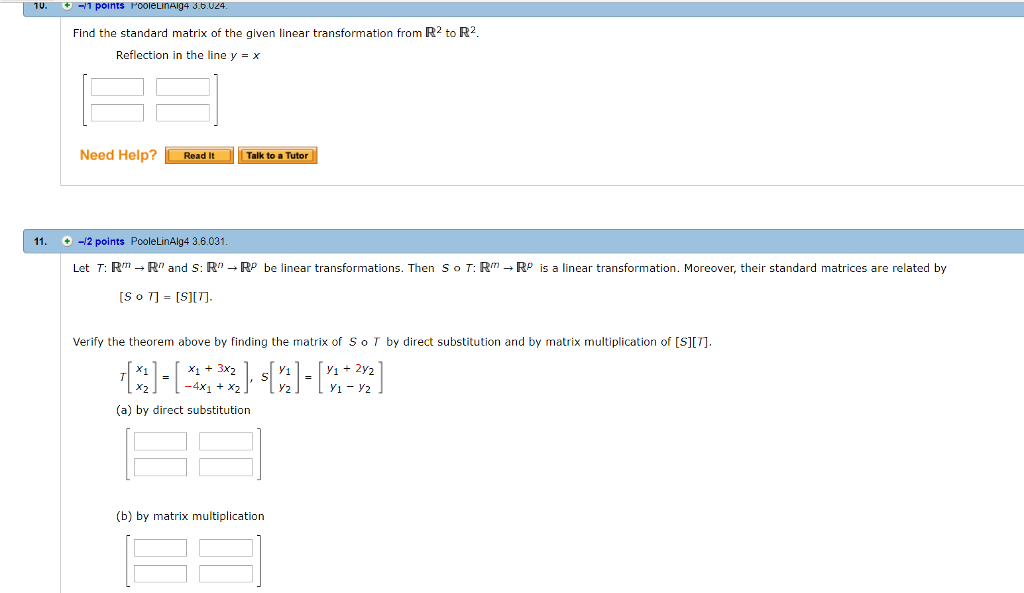



Find The Standard Matrix Of The Given Linear Chegg Com




In This Problem We Are Dealing With Transformations Chegg Com




Matrix Corresponding To Rotation Matrix Corresponding To Reflection Rotation And Reflection Y Tan X Ppt Download




Fp1 Matrices Transformations Ppt Download



2d Reflection In Computer Graphics Definition Examples Gate Vidyalay
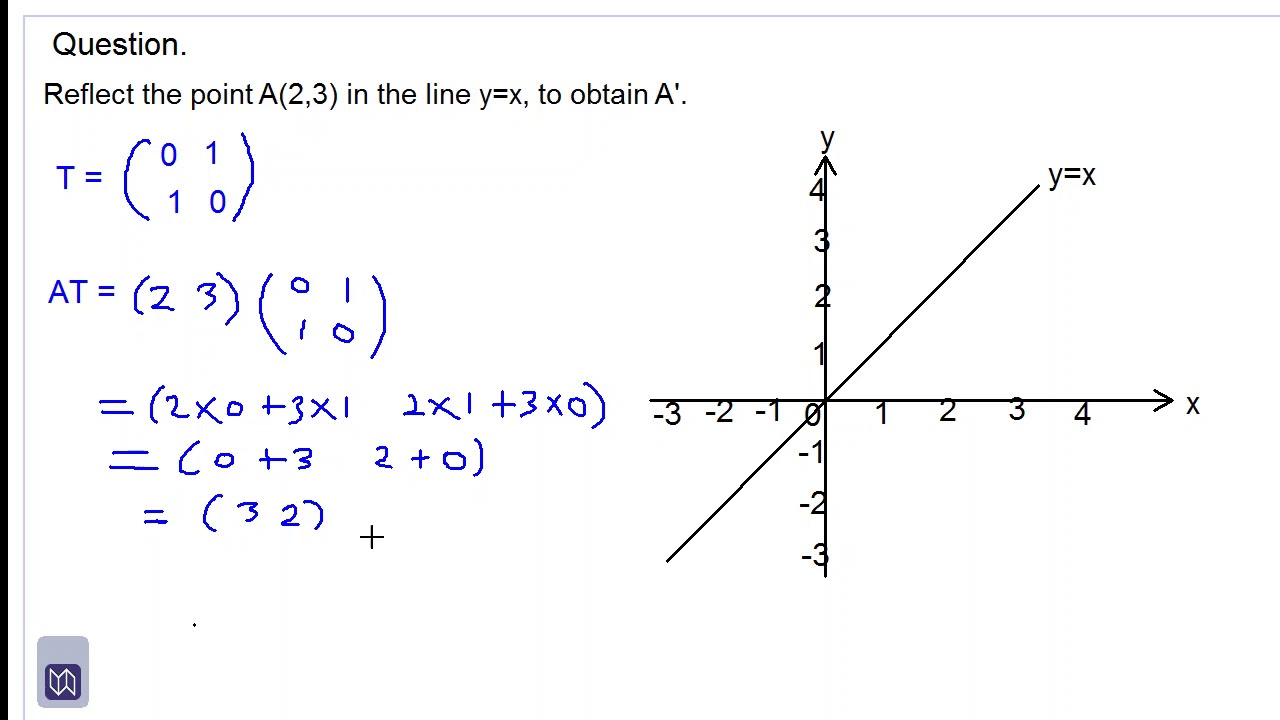



Transformation Matrix For Reflection In Y X Youtube
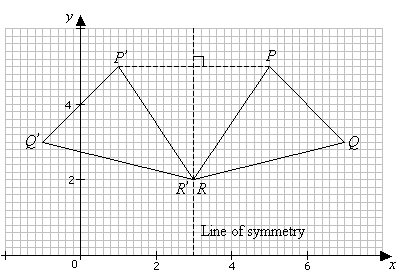



Reflection Transformation Solutions Examples Videos
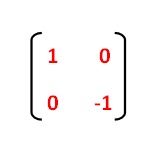



Reflection Transformation Matrix



1



Www2 Clarku Edu Faculty Djoyce Ma130 Lintrans2 Pdf




1 9 The Matrix Of A Linear Transformation
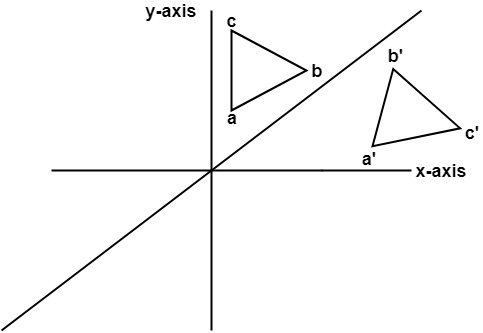



Computer Graphics Reflection Javatpoint



Q Tbn And9gctvjthqkdwbpqfxmfukfqyrhm8wtlbtfnfu2u0osqggs0pct8ms Usqp Cau
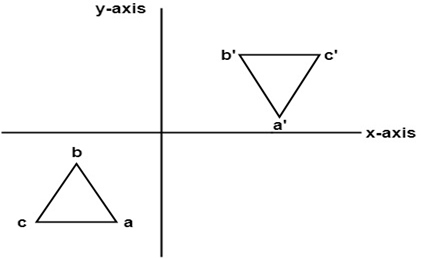



Computer Graphics Reflection Javatpoint




Transformation Using Matrices Geometry Transformations Mathplanet



Determine The Transformation Matrix For The Reflection Computer Graphics
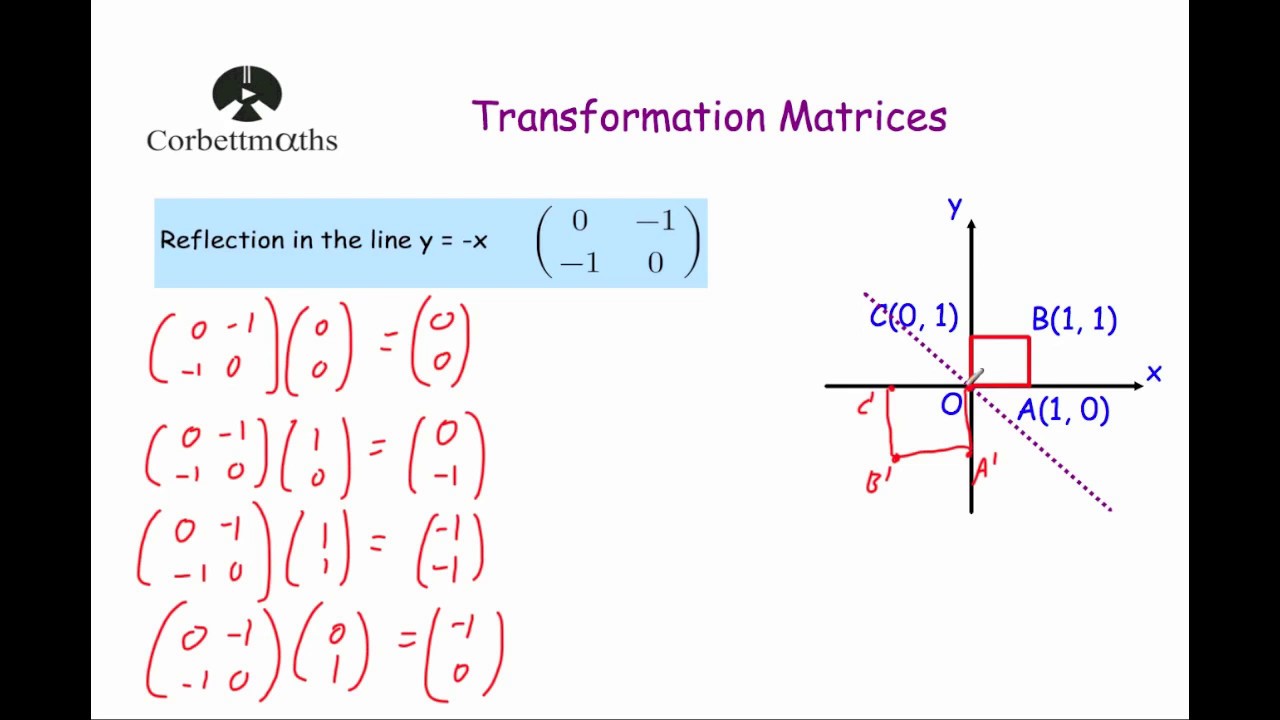



Reflection In The Line Y X Transformation Matrix Youtube



Linear Transformations Reflections Examsolutions




The Line X 0 Novocom Top



1



Matrix Reflections




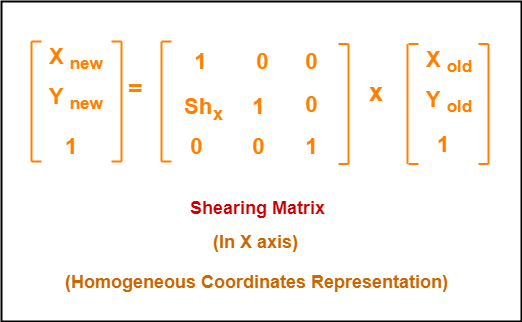
Define The Terms With Example 1 Reflection 2 Shearing




Transformation Matrix Wikipedia
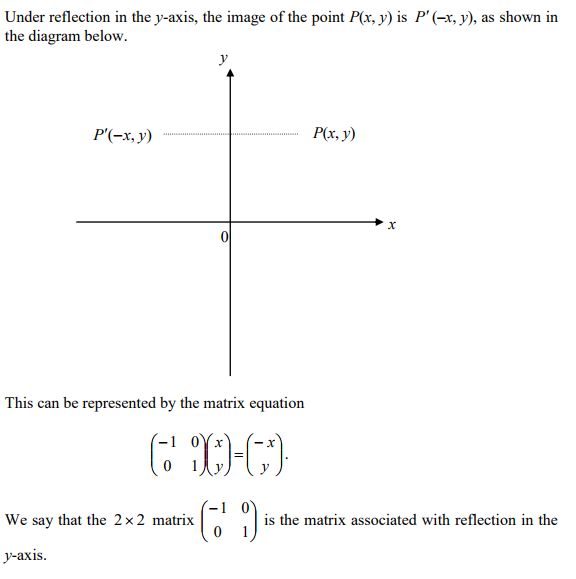



Matrix Transformations Advanced Higher Maths




Reflection Transformation Matrix



Solved Find The Affine Matrix Of The Mirror Reflection Over The Line 1 1 4 Or Y X 4 Course Hero
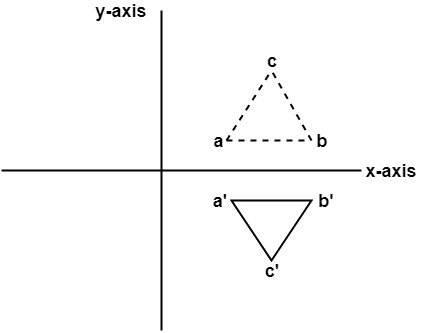



Computer Graphics Reflection Javatpoint
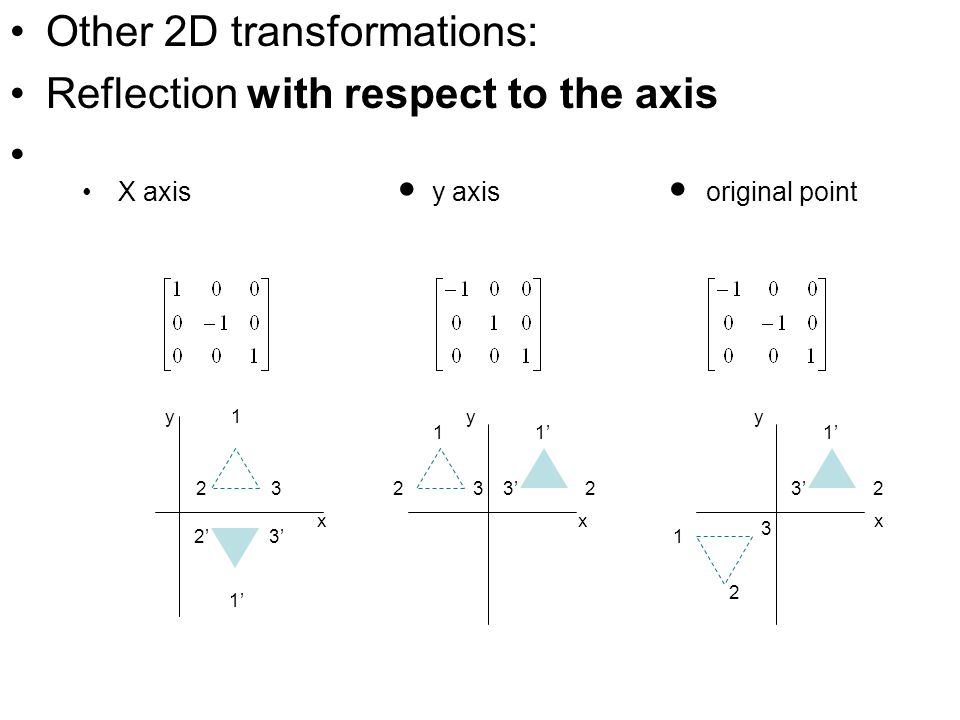



2d Transformation Of Graphics Ppt Video Online Download
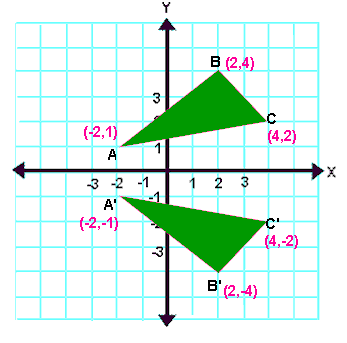



Reflection Transformation Matrix
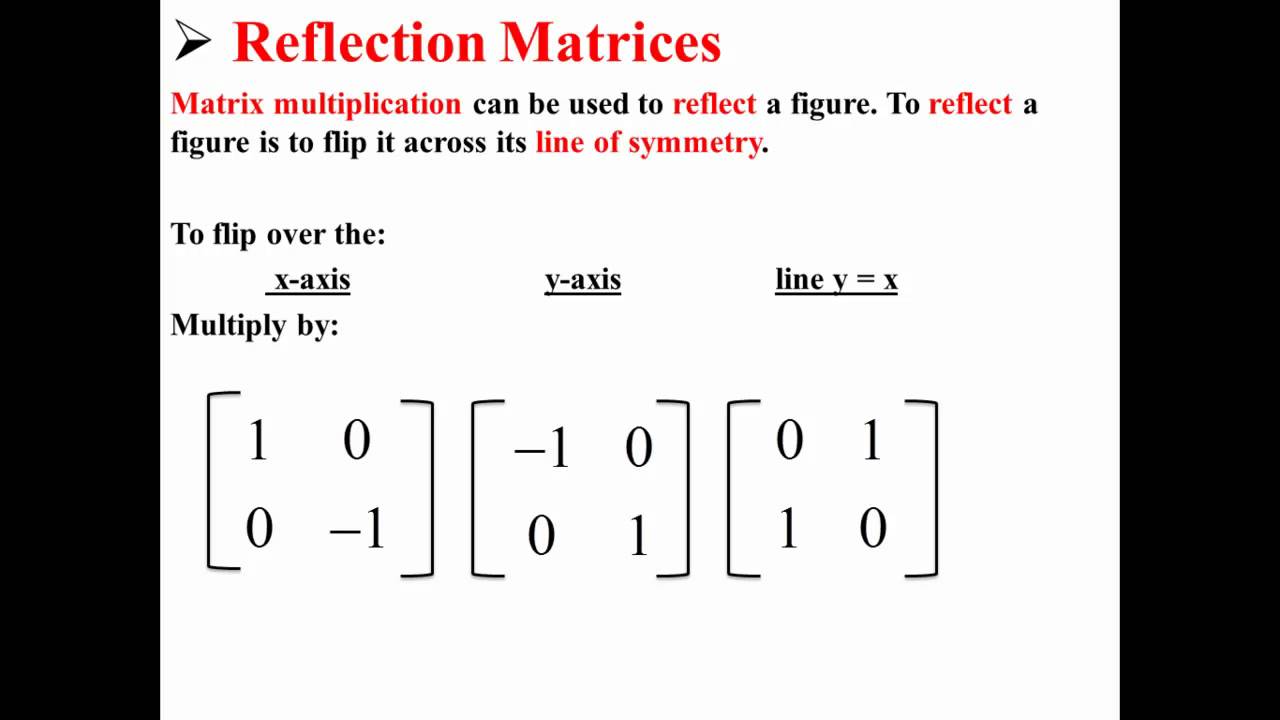



Matrix Reflections Youtube
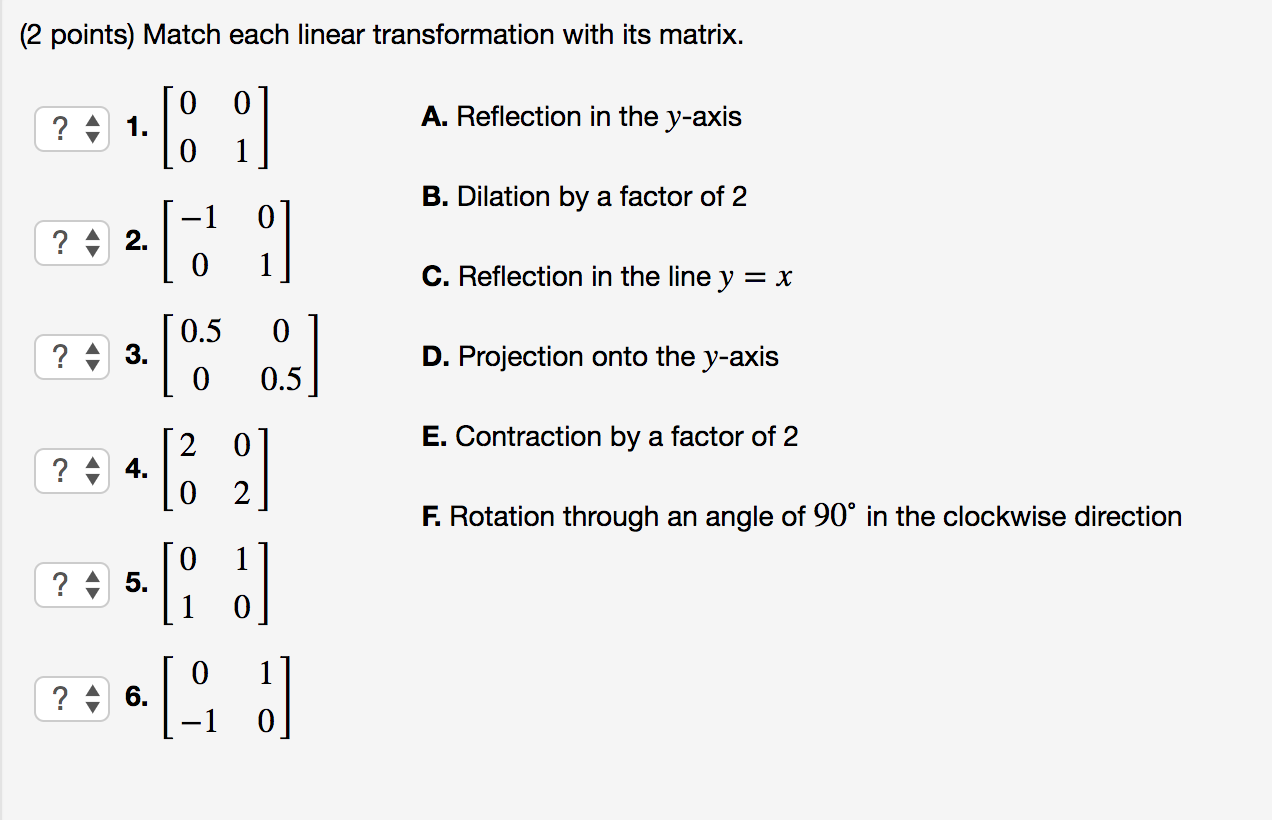



2 Points Match Each Linear Transformation With Its Chegg Com




1 Point Match Each Linear Transformation With Its Chegg Com



1




2d Shearing In Computer Graphics Definition Examples Gate Vidyalay
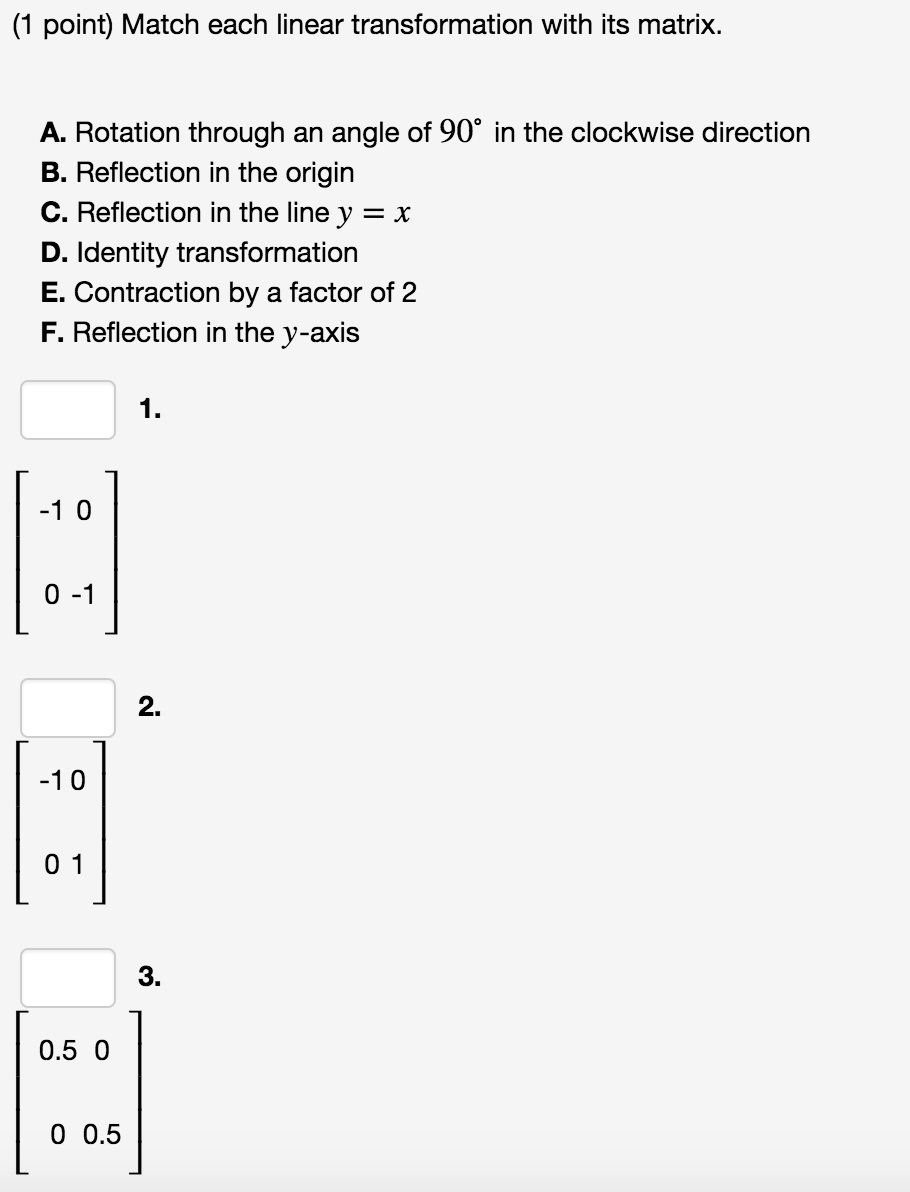



Match Each Linear Transformation With Its Matrix A Chegg Com
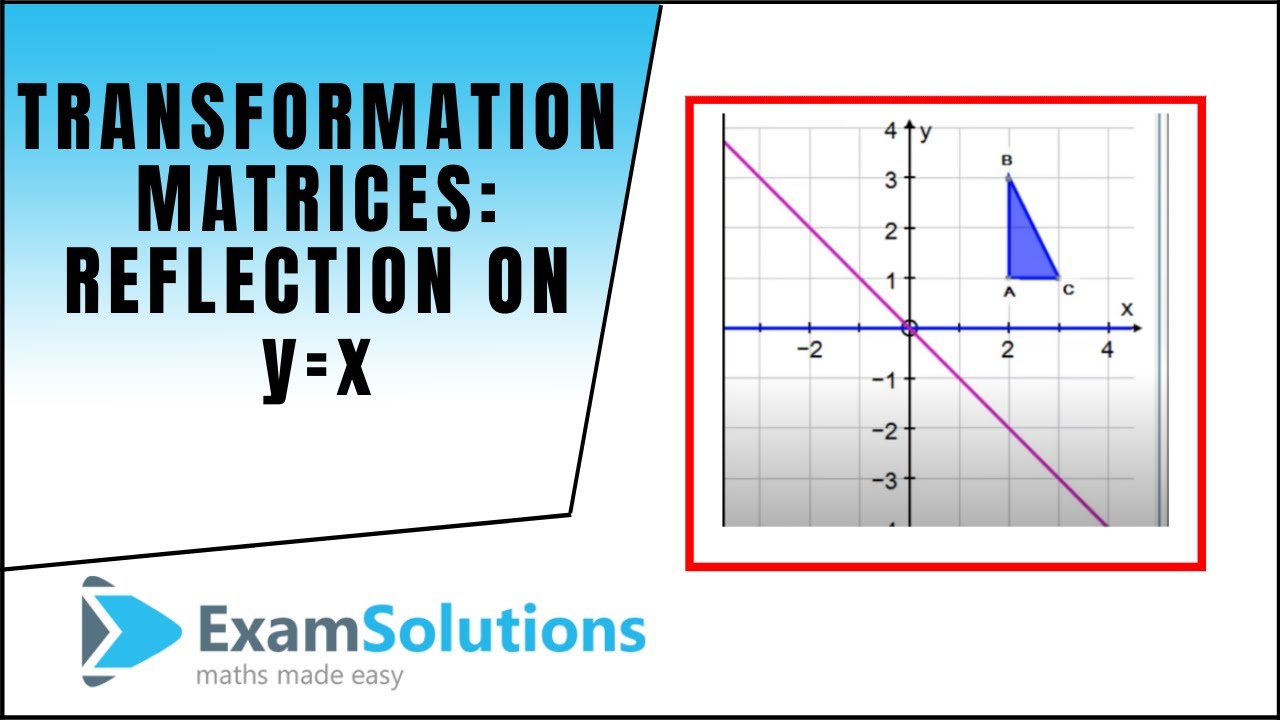



Transformation Matrices Reflection The Line Y X Examsolutions Maths Tutorials Youtube
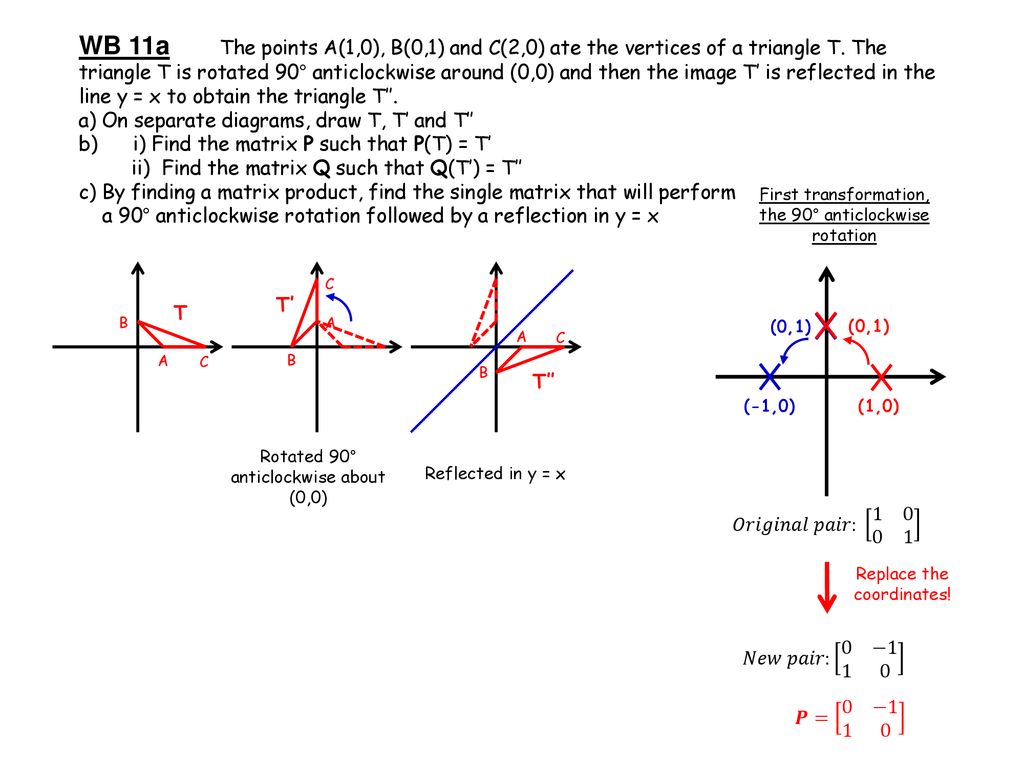



Fp1 Matrices Transformations Ppt Download
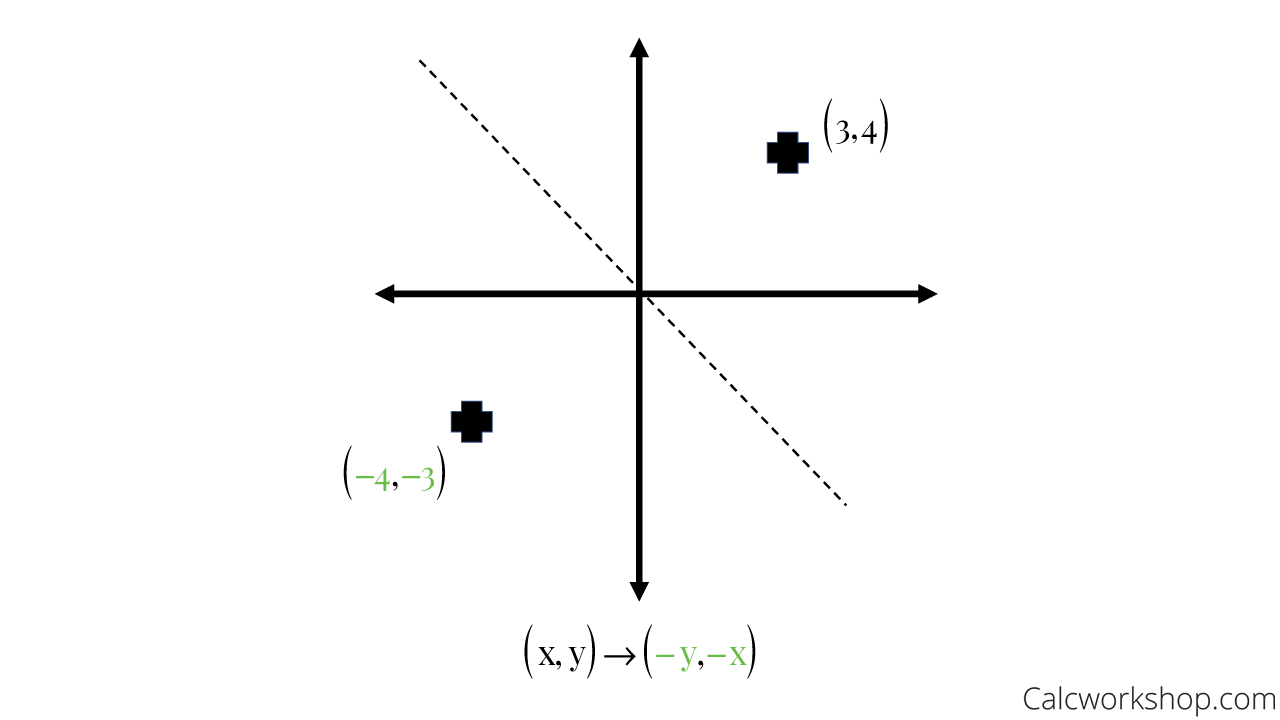



Reflection Rules How To W 25 Step By Step Examples




2d Transformation Tutorialspoint
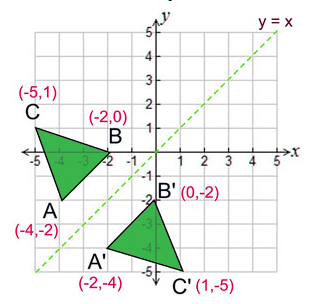



Reflection Definition Reflection In The Coordinate Plane




Chapter 2 Matrices And Linear Transformations 大葉大學 資訊工程系 黃鈴玲 Linear Algebra Ppt Download




The Matrix For The Linear Transformation Of The Reflection Across A Line In The Plane Problems In Mathematics
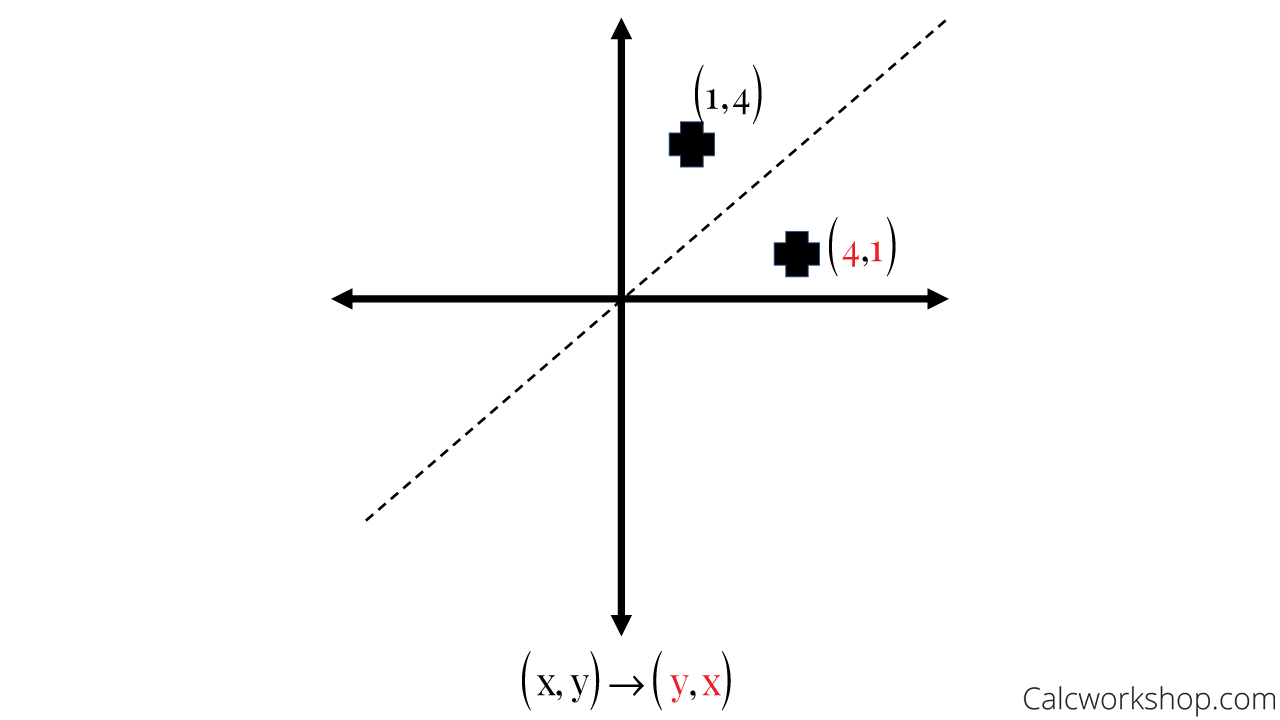



Reflection Rules How To W 25 Step By Step Examples




Computer Graphics 3 D Transformations Translation Rotation Rotation
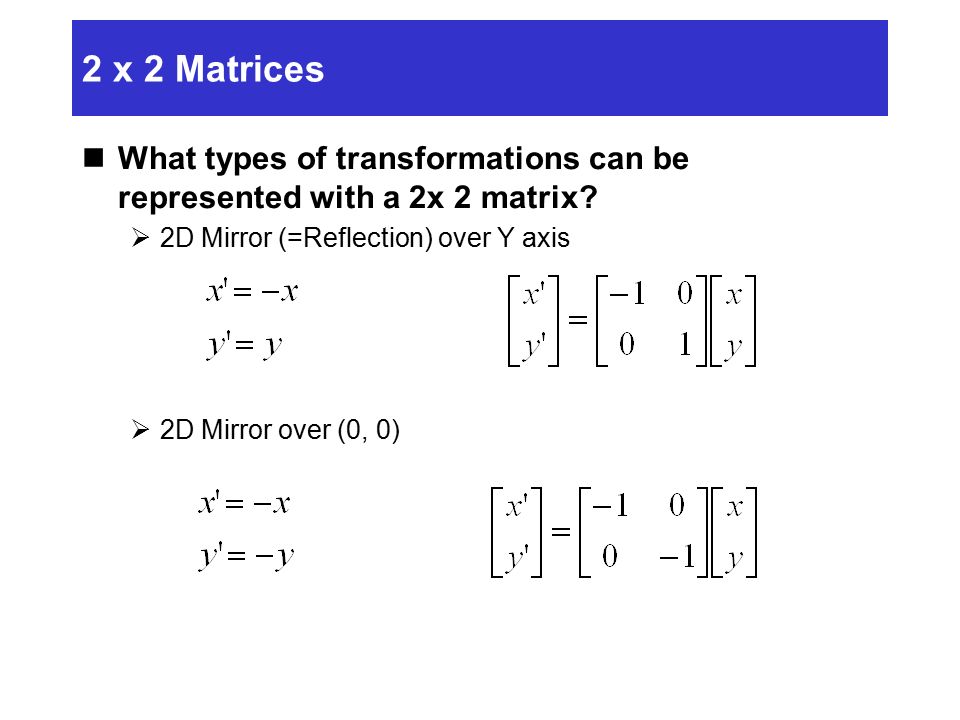



Modeling Transformation Ppt Download




The Useless Perspective That Transformed Mathematics Quanta Magazine
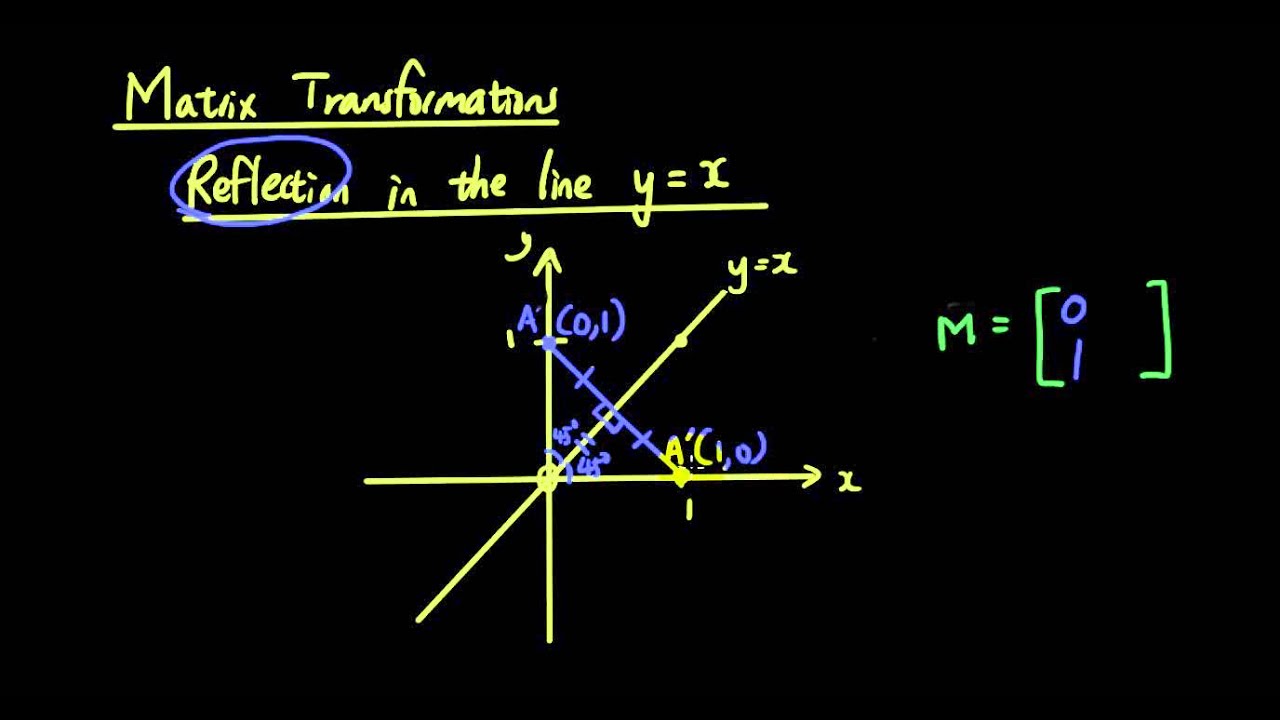



Linear Transformations With Matrices Lesson 10 Reflection In The Line Y X Youtube
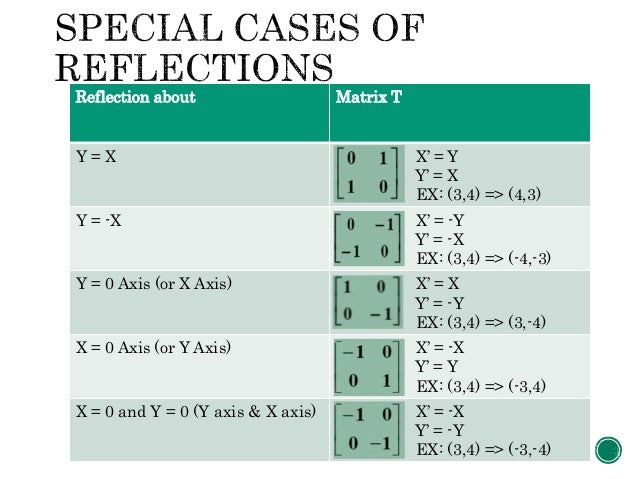



Computer Graphic Transformations In 2d



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿